Before we get started on the semantic web, let’s take a look at how the World Wide Web has evolved.
The biggest feature the web offered when it was invented in 1989 was the hyperlink. It meant that you no longer had to trawl through citations looking for the source material – it was now just one click away and its precise location was no longer important.
From this, we moved on to web 2.0, which is where we are now. We have seen the advent of social media platforms and the rise of independent content creators and mass sharing. However, there is still not total interconnectivity. There are a range of sites on the web which need to be used independently, but the shift is starting as data is being linked and the semantic web is becoming more prominent.
This brings us to web 3.0, which is mistakenly used synonymously with the semantic web. However, web 3.0 has a number of defining features, the semantic web being only one of them:
- Digital assistants (Siri, Google, Cortana, etc.)
- Voice search
- Internet of things
- Use of AI in search results
- The semantic web
Why is the Semantic Web So Good?
The focus of the semantic web has shifted so that it no longer relies on URLs to build relationships between data, but relies instead on the actual context. This allows for a human-esque understanding of data and also better data encryption increasing security on the web.
This allows search engines like Google to better respond to questions. You can already see this happening with snippets and related questions:
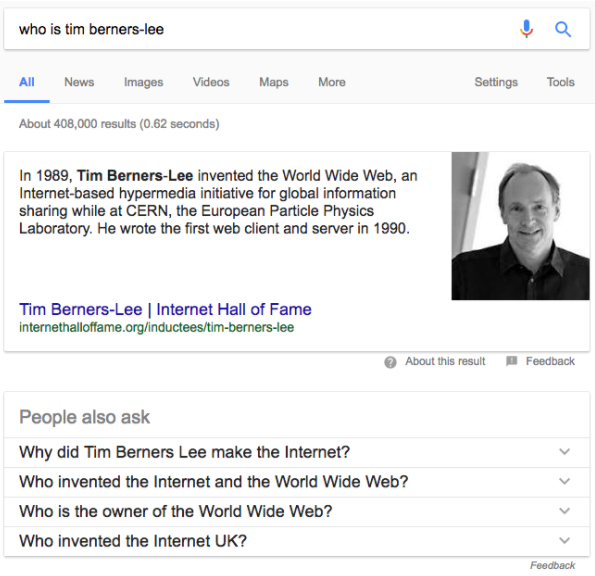
Google Now
Google has created an ecosystem that attempts to bring your entire existence on the web to one place. It will give you cards related to your most frequent searches, link incoming emails to create your schedules (flights, meetings, etc.), remember your home, work and how you travel to give you live travel times, information, and much more.
Google now is making the web more proactive, giving you the information, before you even know that you need it.
More relevant search engines
Searches you make are no longer forgotten, but used to help tune results in the future, making sure that you get exactly what you’re looking for. Google now remembers connections, meaning its users receive relevant information based on their interests. That also means you can get more relevant visitors to your website using semantic SEO techniques.
Business application
Businesses can take advantage of this new tech to create their own semantic web which will help improve three key areas. We’ve gone over the business benefits in a detailed article, but here’s a quick summary:
- Organic Marketing – Make your search results more relevant by understanding that people aren’t using keywords to search anymore, but are looking for solutions to problems. The semantic web will allow you to be more relevant to these searches.
- User Experience – Organise your site based on semantics which will allow for better engagement and ultimately higher conversion rates
- Content Marketing – Using the tenets of the semantic web in your content creation allows for a higher ranking on search engines and again an increased conversion rate.
What’s Holding Us Back?
For the semantic web to succeed, it needs more data to be shared, however people and businesses can be hesitant when sharing all their data. There is a need for a greater community involvement in data sharing, which will ultimately create a better online experience for all. The second big problem is with distinguishing context between shared names, but this should be resolved as the knowledge base grows.
The building blocks for web 3.0 and the semantic web are already in place, it is now up to us to embrace it as it can only flourish with more data being shared.